Phishing basics:
Phishing is a fraudulent technique to trick a person into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials, bank account information, trade secrets, or credit card numbers by posing as a friend or other trusted source (such as your bank or Amazon). You can see a malicious email we received in our own inbox here.
Signs of phishing:
- Contains links or attachments
- Poor grammar and spelling or unusual salutations
- Sense of urgency
- Asks for personal information
- Threatens or rewards
What to do:
- Think before you click
- If it seems phishy, it probably is
- Don’t divulge any personal information
- Verify directly with the source
- Invest in spam protection and employee awareness training
Types of phishing:
Spear phishing
Hyper-targeted (using a spear instead of casting a wide net) to a specific person or business in order to steal personal data or install malware on a computer.
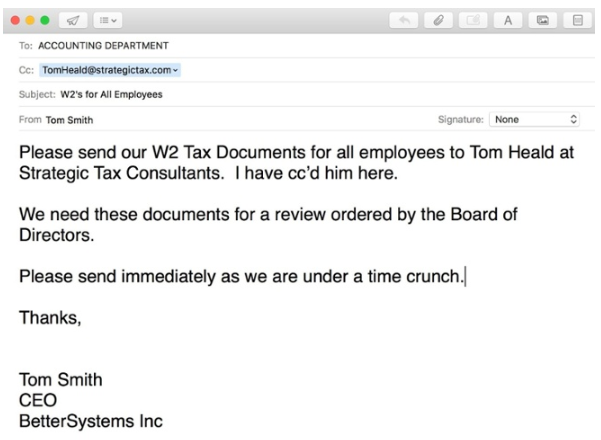
Credit: EDTS
Whaling
Targets the big fish in a company AKA the execs.
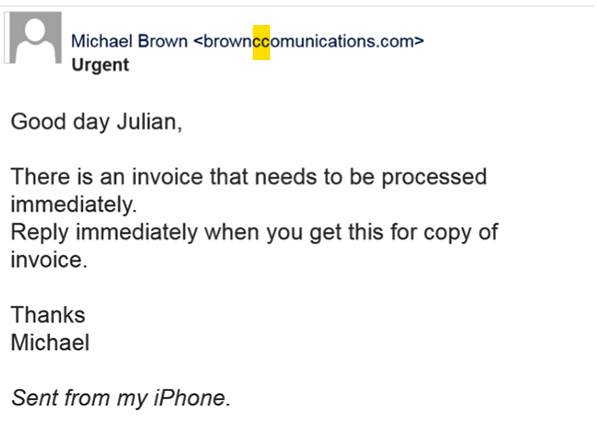
Credit: CSO
Cloning
A legitimate email is copied but the links and/or attachments are replaced with malicious ones.
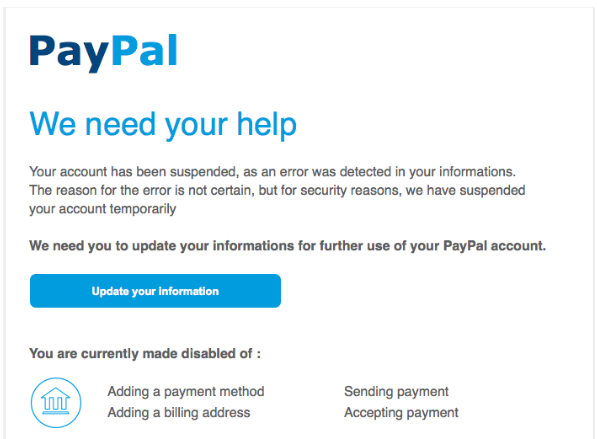
Credit: EDTS
Vishing (voice phishing)
A scammer tries to steal your personal information via phone. They will either call you out of the blue or following up on an email.
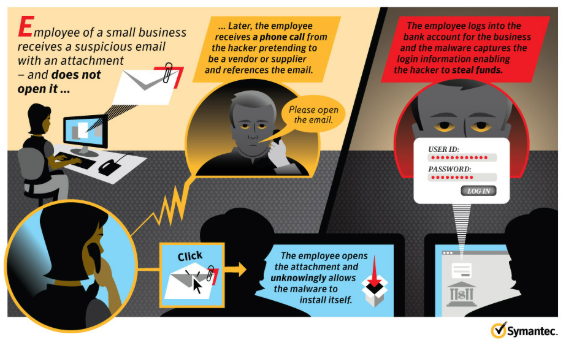
Credit: Symantec
SMShing (SMS phishing)
Phishing via text message, urging a person to click a dangerous link.
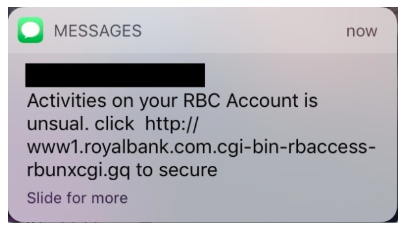
Credit: Malwarebytes Labs






